《计算机系统要素》Day06 构建一个CPU
今天我们通过底层芯片:ALU、MUX、寄存器 构建出 HACK 计算机的核心部件: CPU!
首先我们看看 CPU 的抽象表现形式:
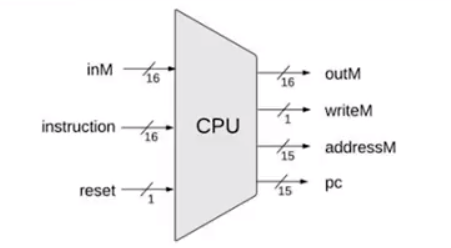
在任意一个时刻,CPU 都有以下两个功能:
- 执行当前指令
- 获取下一条指令(计算下一条指令的位置)
在任意时刻,CPU 都有三个输入:
- RAM 提供的数据
- ROM 提供的指令
- 用户提供的 reset 输入
同样,在任意时刻,CPU 有以下的四个输出:
-
提供给 RAM 的输出:
- 16 位写入数据
- 15 位写入地址
- 是否写入指令
-
提供给 ROM 的输出:
下一时刻请求的指令地址(PC 计数输出)
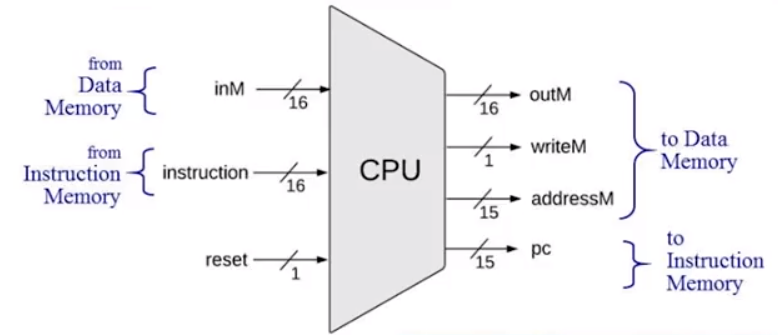
这是 CPU 对外部提供的接口,那么 CPU 的内部实现是什么样子的呢?
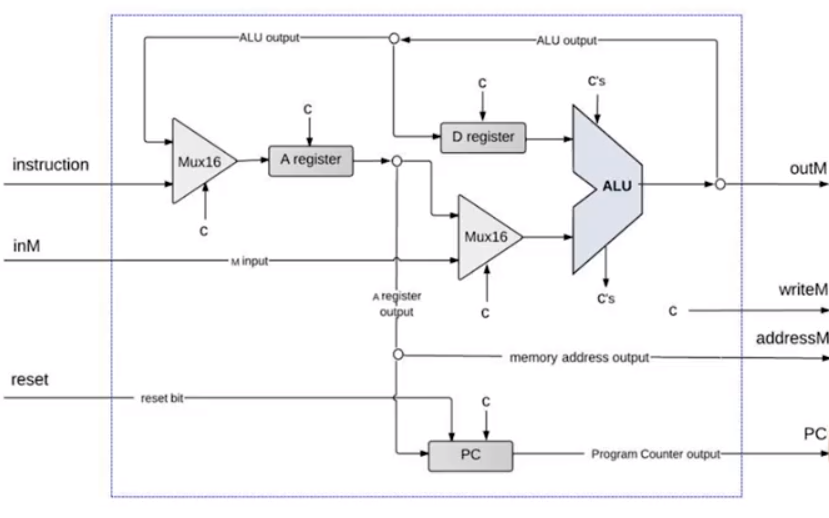
上面给出了 HACK CPU 的一种实现形式
图中给出了 CPU 内部各个部件的接口连线,但未给出控制位,这要求我们在进行 HDL 编写的时候自己实现。
HACK CPU HDL 语言实现
-
首先,我们来尝试实现 CPU 的 A 寄存器部分
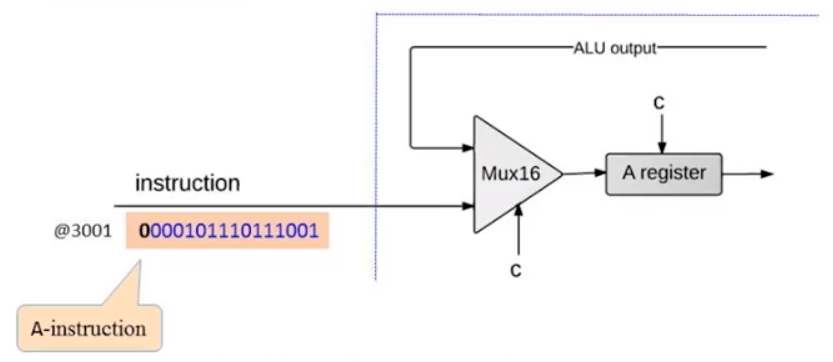
A 寄存器与一个数据选择器相连,该数据选择器用于筛选,A寄存器的数据输入是来自 ALU 还是外部输入的指令。其控制位应该是 instruction[15] 当其为 0 时,MUX 输出 instruction[0..14] .
A 寄存器的输入控制,应该由 instruction 中 A 指令控制位,和 C 指令中写入 A 指令共同决定
最终,这个区域的实现是这样的:
Mux16(a=instruction[0..15], b=ALUoutput, sel=instruction[15], out=Ain); Not(in=instruction[15], out=isAInstruction); Or(a=instruction[5], b=isAInstruction, out=loadA); ARegister(in=Ain, load=loadA, out=Aout); -
接下来,我们实现 D 寄存器:
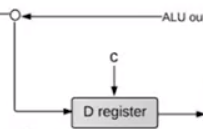
D 寄存器就简单了,只有一个控制位,这个控制位和C指令有关
And(a=instruction[15], b=instruction[4], out=loadD); DRegister(in=ALUoutput, load=loadD, out=Dout);这个也就是 ALU 的数据输入之一
-
接下来,我们实现下一个部件:A、M输入选择器
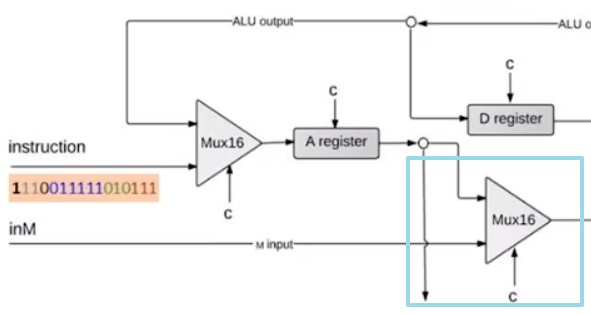
当我们执行 C 指令时,若 instruction[12]=0 表示从 A 寄存器中读取数据。
Mux16(a=Ain, b=inM, sel=instruction[12], out=AMout); -
ALU 的集成
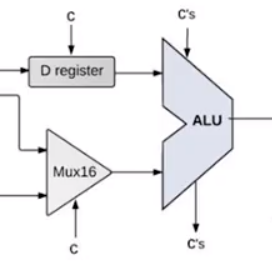
ALU 接受两个数据输入,多个指令输入(instruction[6..11])
ALU(x=Dout, y=AMout, zx=instruction[11], nx=instruction[10], zy=instruction[9], ny=instruction[8], f=instruction[7], no=instruction[6], out=ALUoutput, zr=, ng=); -
PC 的集成
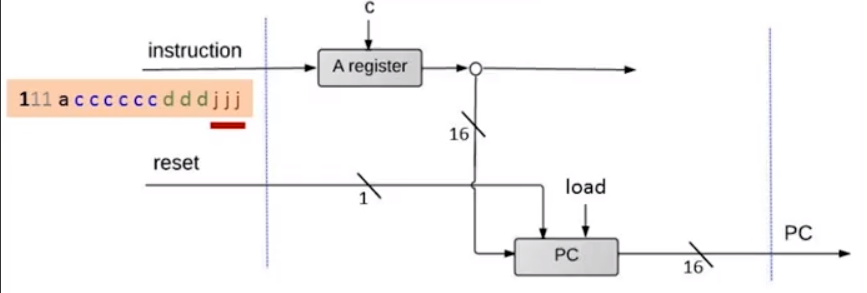
PC 芯片我们之前实现过,他有四个输入位:
- in 跳转地址输入
- inc 判断是否进行增一
- load 判断是否载入 in 地址
- reset 判断是否清零
后三个控制位权重依次增高
HDL 实现如下:
Not(in=ng, out=ps); And(a=instruction[0], b=ps, out=psJMP); And(a=instruction[1], b=zr, out=zrJMP); And(a=instruction[2], b=ng, out=ngJMP); Or(a=psJMP, b=zrJMP, out=JMP0); Or(a=JMP0, b=ngJMP, out=loadPC); PC(in=Aout, load=loadPC, inc=true, reset=reset, out=pc); -
输出引出:
And(a=instruction[15], b=instruction[3], out=writeM); Mux16(a=ALUoutput, b=false, sel=false, out=outM); Mux16(a=Aout, b=false, sel=false, out=addressM); -
测试:
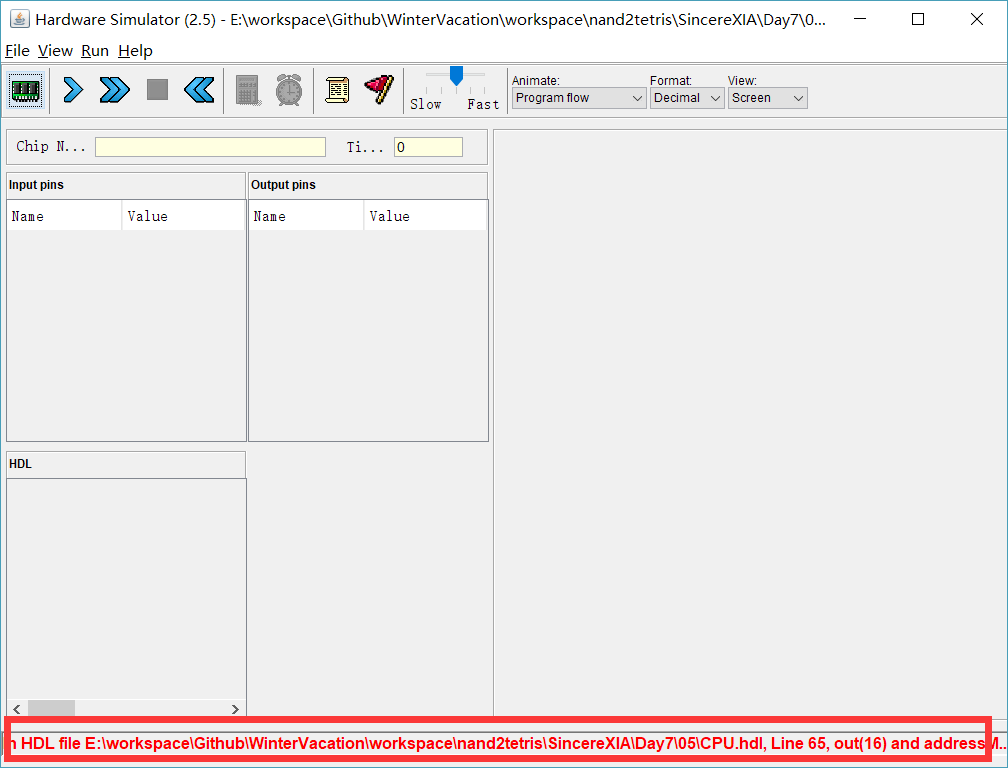
可以看到,地址位的长度不一致,我们得把16位地址,取后部15位输出,为了实现这个功能,我们设计了一个外部芯片:
CHIP C16to15 { IN in[16]; OUT out[15]; PARTS: Mux(a=in[0], b=false, sel=false, out=out[0]); Mux(a=in[1], b=false, sel=false, out=out[1]); Mux(a=in[2], b=false, sel=false, out=out[2]); Mux(a=in[3], b=false, sel=false, out=out[3]); Mux(a=in[4], b=false, sel=false, out=out[4]); Mux(a=in[5], b=false, sel=false, out=out[5]); Mux(a=in[6], b=false, sel=false, out=out[6]); Mux(a=in[7], b=false, sel=false, out=out[7]); Mux(a=in[8], b=false, sel=false, out=out[8]); Mux(a=in[9], b=false, sel=false, out=out[9]); Mux(a=in[10], b=false, sel=false, out=out[10]); Mux(a=in[11], b=false, sel=false, out=out[11]); Mux(a=in[12], b=false, sel=false, out=out[12]); Mux(a=in[13], b=false, sel=false, out=out[13]); Mux(a=in[14], b=false, sel=false, out=out[14]); }我们把需要适配的输出重写一下:
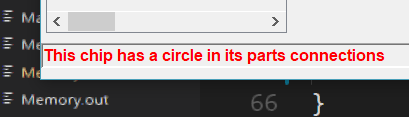
发现一个小错误:

修正:
最终结果:
然后:
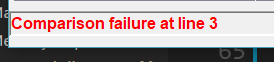
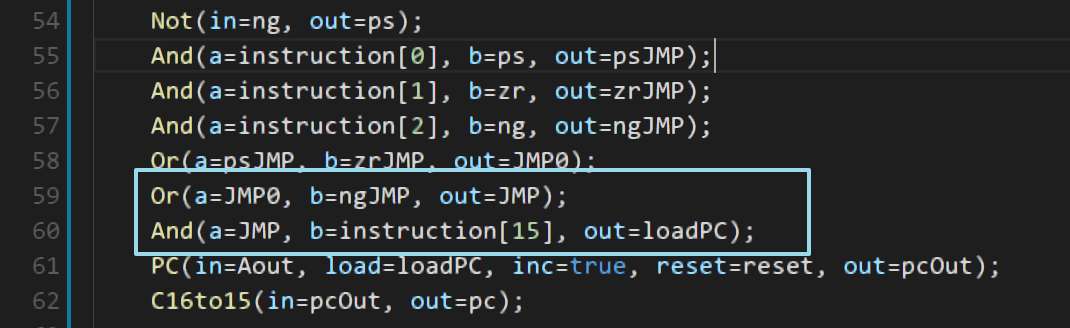
又出错了,观察发现是 loadPC 有问题,调整一下:
跑到第61行又炸了:
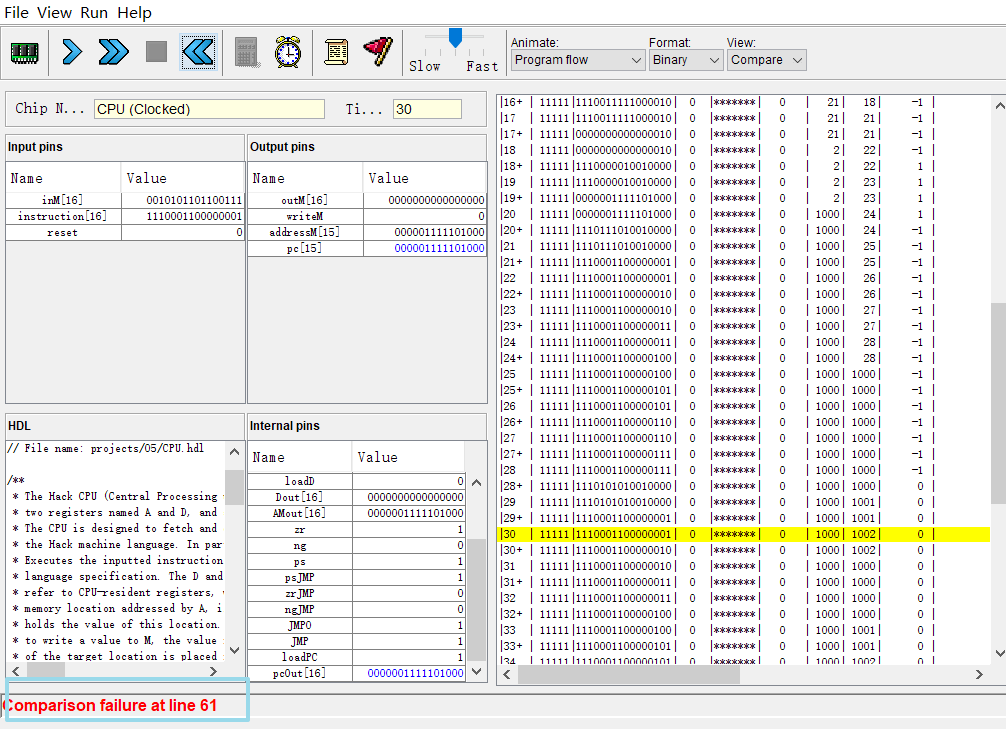
嗯,看了一下内部管脚,正数判断有问题(不是负数不代表就是正数。。。)
再修改一下下:
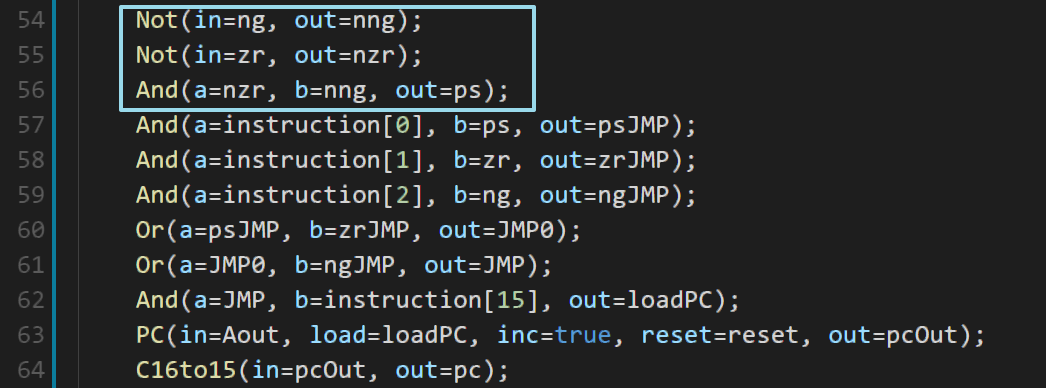
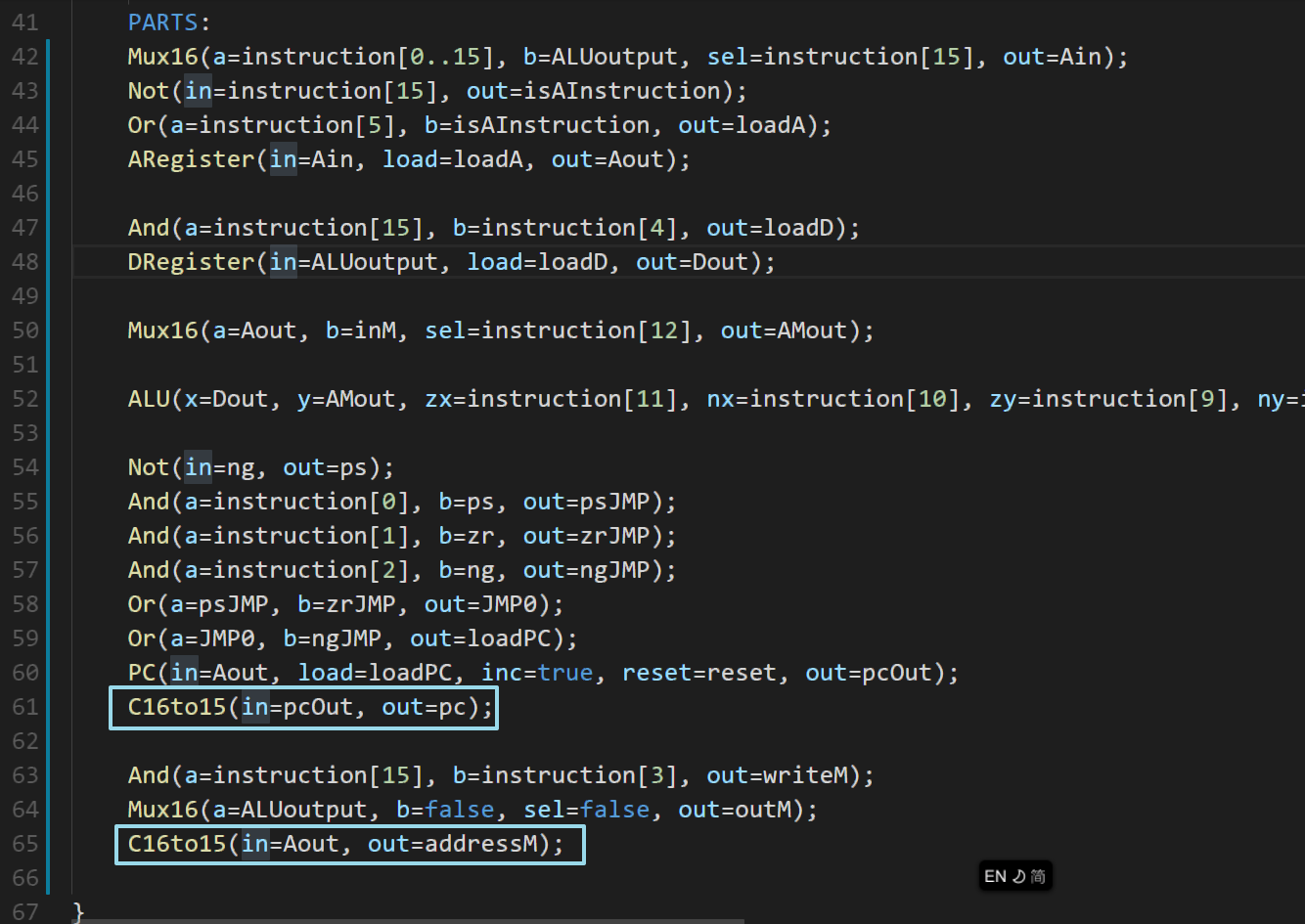
最终结果:
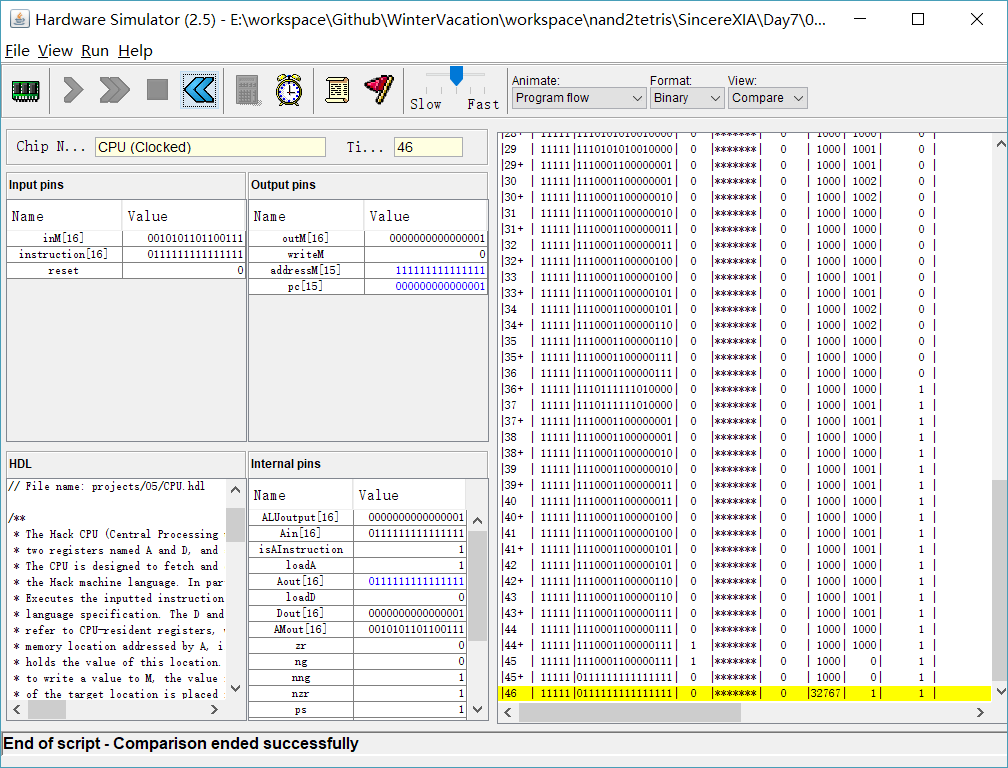
谢天谢地!!!
最终整个 CPU HDL 代码:
CHIP CPU { IN inM[16], // M value input (M = contents of RAM[A]) instruction[16], // Instruction for execution reset; // Signals whether to re-start the current // program (reset==1) or continue executing // the current program (reset==0). OUT outM[16], // M value output writeM, // Write to M? addressM[15], // Address in data memory (of M) pc[15]; // address of next instruction PARTS: Mux16(a=instruction[0..15], b=ALUoutput, sel=instruction[15], out=Ain); Not(in=instruction[15], out=isAInstruction); Or(a=instruction[5], b=isAInstruction, out=loadA); ARegister(in=Ain, load=loadA, out=Aout); And(a=instruction[15], b=instruction[4], out=loadD); DRegister(in=ALUoutput, load=loadD, out=Dout); Mux16(a=Aout, b=inM, sel=instruction[12], out=AMout); ALU(x=Dout, y=AMout, zx=instruction[11], nx=instruction[10], zy=instruction[9], ny=instruction[8], f=instruction[7], no=instruction[6], out=ALUoutput, zr=zr, ng=ng); Not(in=ng, out=nng); Not(in=zr, out=nzr); And(a=nzr, b=nng, out=ps); And(a=instruction[0], b=ps, out=psJMP); And(a=instruction[1], b=zr, out=zrJMP); And(a=instruction[2], b=ng, out=ngJMP); Or(a=psJMP, b=zrJMP, out=JMP0); Or(a=JMP0, b=ngJMP, out=JMP); And(a=JMP, b=instruction[15], out=loadPC); PC(in=Aout, load=loadPC, inc=true, reset=reset, out=pcOut); C16to15(in=pcOut, out=pc); And(a=instruction[15], b=instruction[3], out=writeM); Mux16(a=ALUoutput, b=false, sel=false, out=outM); C16to15(in=Aout, out=addressM); }
_(:3 」∠)_